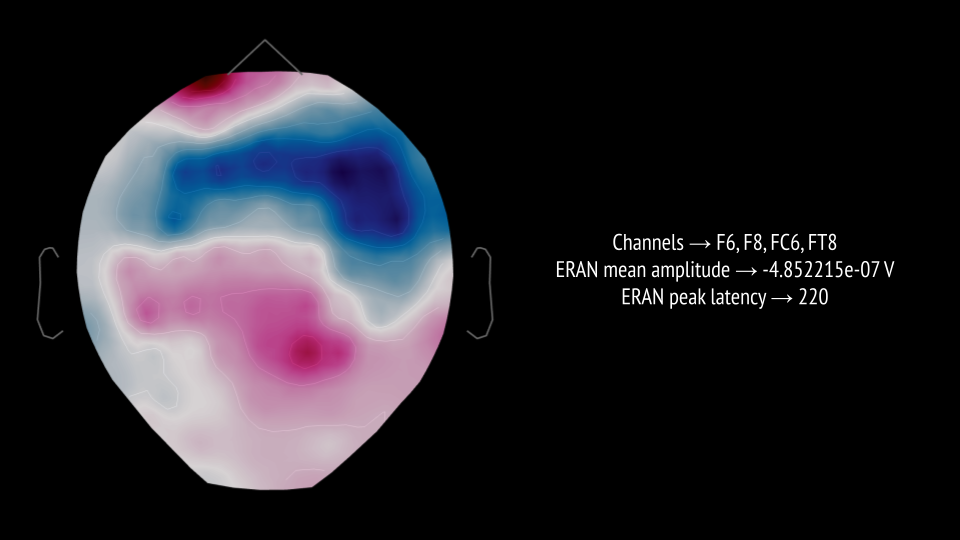
Temporal Decay of Tonal Expectations: ERAN Responses to In-Key and Out-of-Key Stimuli
Temporal Decay of Tonal Expectations: ERAN Responses to In-Key and Out-of-Key Stimuli is an EEG study examining how musical expectations persist and decay across silent interruptions. We measured the Early Right Anterior Negativity (ERAN)—an event-related potential occurring ~150–250 ms after stimulus onset that indexes automatic music-syntactic processing—elicited by in-key and out-of-key tones following short (3 s) and long (8.5 s) silent intervals after a brief melodic context.
Results showed larger ERAN amplitudes for out-of-key tones following shorter silences, consistent with stronger internally maintained tonal frameworks, and reduced responses after longer delays, suggesting temporal decay of tonal memory. While not statistically significant due to limited sample size, the study motivates refined paradigms for probing predictive processing, tonal expectancy, and memory persistence in discontinuous musical streams.
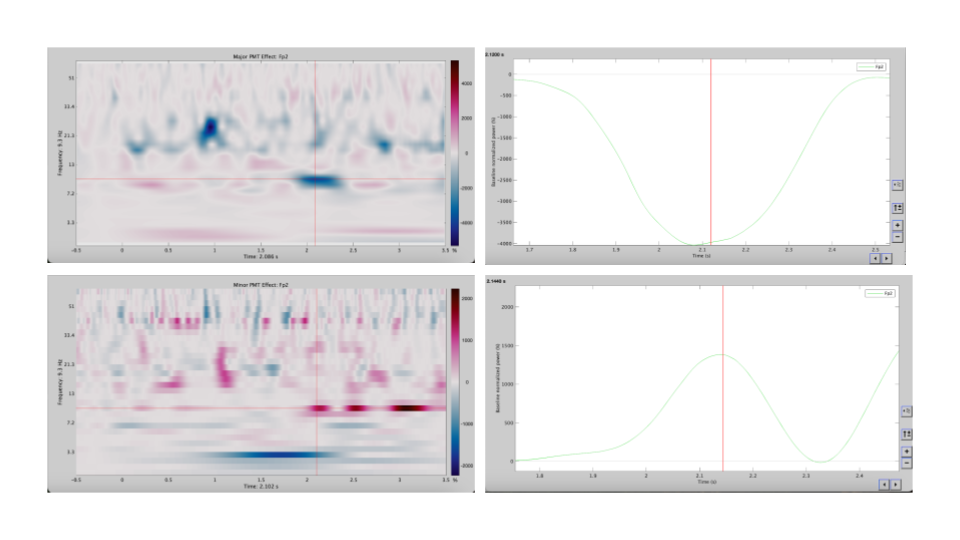
Induced oscillatory dynamics during musical mode transitions
Induced Oscillatory Dynamics During Musical Mode Transitions investigates how the brain allocates attention when musical expectations are violated. Using EEG time–frequency analysis, we examined induced alpha-band oscillations (8–12 Hz), a neural signature associated with attentional gating and sensory processing, during congruent mode transitions (major to major, minor to minor) and incongruent transitions (major to minor, minor to major).
Results showed stronger alpha event-related desynchronization (ERD) during incongruent transitions, particularly for major-to-minor shifts, indicating increased attentional engagement in response to unexpected harmonic changes. Alpha modulation emerged earlier than ERP markers such as ERAN, suggesting that induced oscillatory activity captures complementary and temporally earlier mechanisms underlying musical expectancy and tonal hierarchy processing.